Biogas is methane rich gas that is produced by anaerobic digestion of organic material such as manure, sewage sludge and other organic waste fractions from industries and households. It represents a renewable energy source and plays an important part in the green transition as it can replace natural gas. Biogas production can thus be perceived as a combined green energy production and a waste treatment technology. When manure is used for biogas production, the emissions of greenhouse gasses from handling and storage of slurry are reduced. Also, biogas production serves as a means to recirculate the nutrients that are in the input biomass.
Biogas production and use
The production of biogas in Denmark has increased rapidly since the 2012 when a new subsidy scheme entered into force. The subsidy scheme, which include a fixed subsidy level across eligible biogas producers, was targeted at increasing the production of biogas for electricity production, processing, heat production and upgrading to biomethane, where the latter is to be injected into the gas system, where it displace natural gas. The subsidy scheme implemented in 2012 was closed for new applications in 2018, but as subsidies were granted for a 20-year period the major share of biogas produced in Denmark today is still subsized.
See the subsidy levels for the current subsidy schemes here: Biogas subsidy levels
Currently there are no subsidy schemes available for new production capacity, but a series of tenders for the production of biogas and other green gases is planned. The choice of the tender approach reflects that the biogas sector in Denmark is now well past the development stage, and accordingly focus is now more on ensuring the efficiency of future biogas production. Subsidization following the tender approach is expected to lower the subsidy per GJ produced compared to the previous scheme.
The Danish Energy Agency is responsible for the rules and regulations regarding the different support schemes and administers the payment of subsidies.
Figure 1 shows how biogas production has developed since 2012, and how it is expected to develop towards 2035 (KF24).
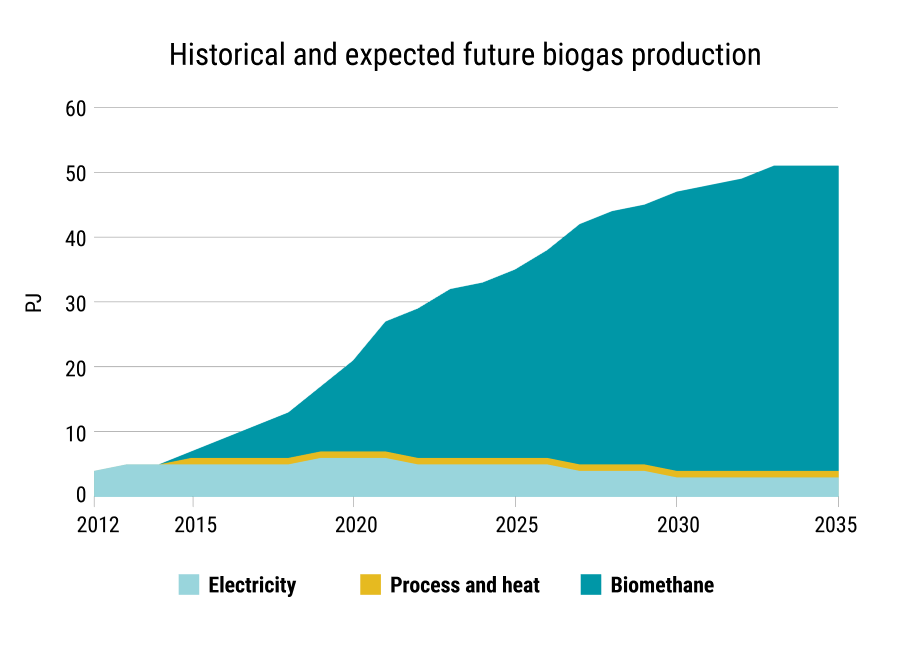
Previously, the major share of biogas was used for electricity production, but today around 80 pct. is upgraded and feed into the natural gas grid, and this development towards upgrading is expected to continue in the future. In 2023 the share of biomethane in the Danish gas system reached almost 40 pct. and by 2030 Danish gas consumption is expected to be 100 pct. green.
Read more about the role of biogas in the green transition: Green Gas Strategy
Biogas plants
Based on the type of input biogas plants can be divided into 4 different types; agricultural plants, sewage plants, industrial plants and landfill plants. Agricultural plants, where livestock waste constitutes the major input, accounted for approximately 85 pct. of biogas production in 2022, and it is also at agricultural plants that future production increases are expected to take place.
The majority of biogas plants are located in the western part of Denmark where livestock density is highest. The Danish Energy Agency has produced a map showing the location, plant type and approximate production capacity of Danish biogas plants. The map is updated in 2023.
Methane loss from biogas plants
Results of a study from 2021 commissioned by the Danish Energy Agency showed that the average annual methane loss from Danish biogas production was around 2.5 pct. The lowest average loss was estimated for larger agricultural plants (1.9 pct.), while sewage plants exhibited the highest average loss (7.7 pct.). To address the loss of methane, which reduce the positive climate effect of biogas, new regulation entered into force 1 January 2023. In the regulation it is specified that all agricultural, sewage and industrial biogas plants are required to implement a self-monitoring programme and to have their plant inspected for methane leaks once a year by an independent and verified third party.
Biomass input and biogas production
Danish biogas plants are obligated to report their biomass use to the Danish Energy Agency once a year. The reports contain information on amounts, types and origin of the biomasses. Most of the biomasses used for biogas production are domestic resources, which if not used for biogas production would either have been incinerated or used directly on the fields as fertilizer.
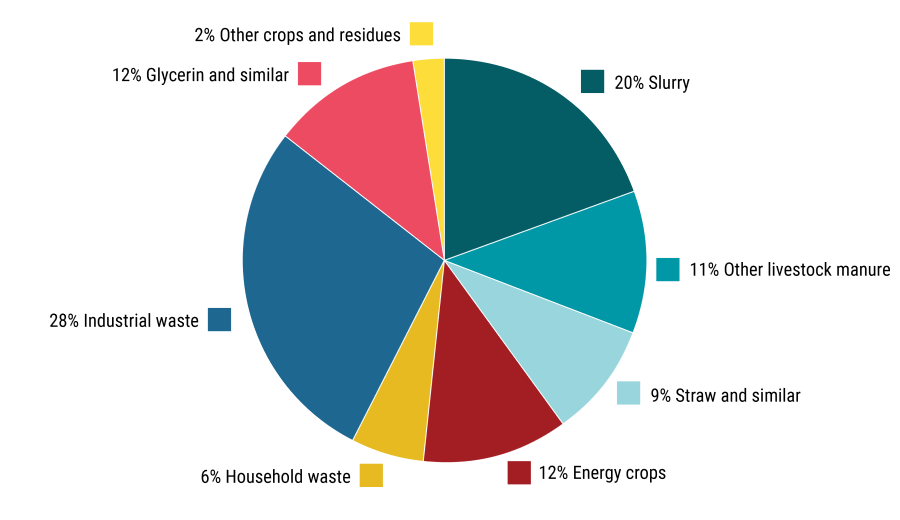
Livestock waste constitutes around 75 pct. of biomass input at agricultural biogas plants. When livestock waste is used as input to biogas production, greenhouse gas emissions are reduced, while the plant availability of nutrients in the biomass is often improved. The remaining 25 pct. comprises different organic waste fractions from households and industry, plus straw and energy crops.
The type of biomass used in the production impacts the sustainability and climate effect of the biogas.
Energy crops such as corn, sugar beets and grass are ideal for boosting biogas production, and many biogas plants include energy crops in their input mix. However, using energy crops entails a reduction in the climate effect of biogas production, which is problematic seen from a sustainability perspective. Accordingly, regulation limiting the use of energy crops for biogas production has been implemented, and the limit is tightened regularly. Valid from 2025 the maximum input share of energy crops is set to 4 pct. and the use of corn is prohibited. The long-term goal is to reduce use of energy crops even further, but regulation beyond 2026 remains to be decided.
Straw constitute a relatively small share of total biomass input, but the share is increasing and, looking forward, straw is expected to play an important role in terms of reaching the target that Danish gas consumption should be 100 pct. green by 2030.
Figure 2 shows biomass input composition of agricultural biogas plants, and Figure 3 shows the estimated share of total biogas production attributable to biomass categories.
Figure 2 Biomass input composition at agricultural biogas plants, 2021-2022.
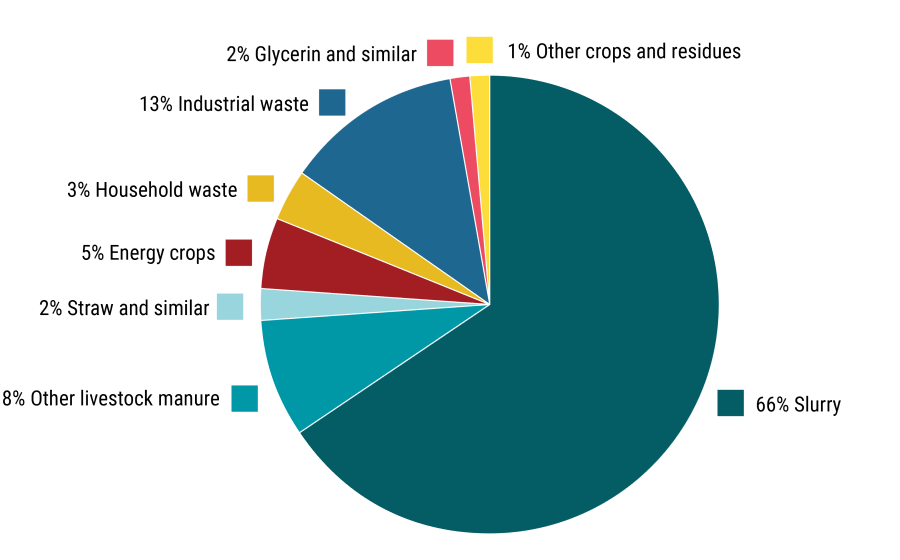
Figure 3 Estimated share of biogas production attributable to different biomass categories, 2021-2022.